Facility Layout and Design
Facility layout and design refer to the process of planning and arranging the physical layout of a facility to optimize efficiency, productivity, safety, and functionality. It involves determining the spatial arrangement of various components within a facility, such as workstations, equipment, storage areas, aisles, and support facilities, to create an optimal workflow and operational environment. Here are the key aspects and considerations involved in facility layout and design:
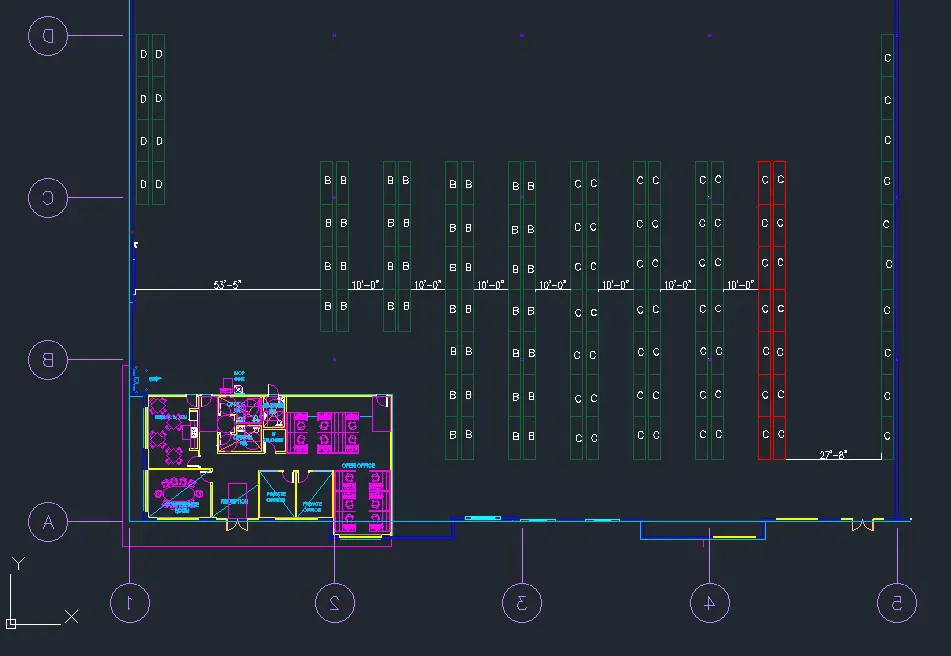
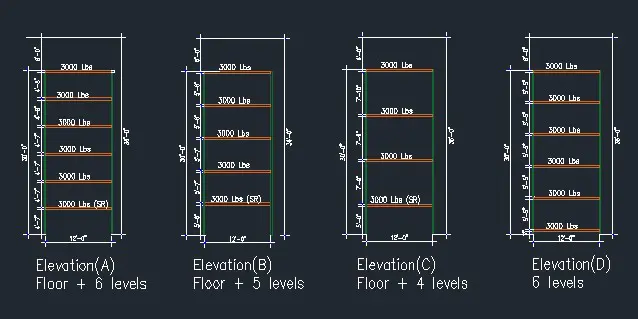
Key Aspects
-
Space Utilization: Maximizing the efficient use of available space within the facility while ensuring adequate room for movement, equipment operation, and storage.
-
Workflow Optimization: Designing the layout to facilitate smooth and efficient workflow processes, minimizing unnecessary movement, congestion, and delays.
-
Safety and Ergonomics: Incorporating ergonomic principles and safety measures into the layout to minimize the risk of accidents, injuries, and ergonomic-related issues among workers.
-
Flexibility and Scalability: Designing a layout that is flexible and adaptable to accommodate changes in production processes, technology, and business requirements over time.
-
Aesthetics and Environmental Factors: Considering aesthetic considerations, environmental factors, and sustainability principles to create a pleasant, comfortable, and environmentally friendly work environment.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring compliance with relevant building codes, safety regulations, zoning requirements, and industry standards governing facility design and construction.
Considerations
-
Process Flow Analysis: Conduct a thorough analysis of workflow processes, material flow, and production requirements to identify opportunities for improvement and optimization.
-
Space Planning: Determining the spatial requirements for different activities, departments, and equipment within the facility and allocating space accordingly.
-
Equipment Layout: Arranging machinery, equipment, and workstations in a logical and efficient manner to minimize handling, transportation, and setup times.
-
Material Handling: Designing efficient material handling systems, such as conveyor belts, forklift routes, and storage systems, to streamline the movement of materials and goods throughout the facility.
-
Storage and Inventory Management: Planning storage areas, racks, shelves, and bins to optimize inventory management, accessibility, and space utilization.
-
Support Facilities: Allocating space for support facilities such as restrooms, break rooms, offices, meeting rooms, and maintenance areas to meet the needs of employees and operational requirements.
-
Safety Measures: Incorporating safety features such as fire exits, emergency lighting, first aid stations, and safety barriers to ensure a safe working environment for employees.
-
Technology Integration: Integrating technology systems such as automation, robotics, and digital monitoring tools into the facility layout to enhance productivity, efficiency, and data-driven decision-making.
Process
-
Needs Assessment: Conduct a thorough assessment of business needs, operational requirements, and future growth projections to inform the facility layout and design process.
-
Conceptual Design: Develop conceptual layout plans and design concepts based on the needs assessment, considering factors such as workflow, space requirements, and operational goals.
-
Detailed Design: Refining the conceptual design into detailed layout plans, incorporating feedback from stakeholders, engineers, architects, and other relevant parties.
-
Implementation: Executing the construction and installation of the facility layout according to the approved design plans, ensuring adherence to timelines, budgets, and quality standards.
-
Testing and Optimization: Testing the functionality and efficiency of the facility layout in real-world operations, making adjustments and optimizations as needed to improve performance.
-
Maintenance and Upkeep: Regularly assessing and maintaining the facility layout to address wear and tear, accommodate changes in operations, and ensure continued efficiency and safety.
Benefits
-
Increased Efficiency: Optimized layout designs can improve workflow efficiency, reduce material handling times, and enhance overall productivity.
-
Cost Savings: Efficient facility layouts can minimize waste, reduce operating costs, and optimize resource utilization, resulting in cost savings for the organization.
-
Enhanced Safety: Well-designed layouts prioritize safety measures, reducing the risk of accidents, injuries, and ergonomic-related issues among workers.
-
Improved Morale: A well-designed facility layout can contribute to a positive work environment, enhancing employee satisfaction, morale, and retention.
-
Adaptability and Scalability: Flexible layout designs allow for easy adaptation to changing business needs, technological advancements, and market dynamics, ensuring long-term viability and growth.
In summary, facility layout and design are critical components of operational efficiency and success, requiring careful planning, analysis, and implementation to create optimal working environments that support productivity, safety, and growth.
